The Profession of Radiography
What is Radiography?
Medical radiography is a broad term that covers several types of studies that require the visualization of the internal parts of the body using X-ray techniques. Radiography means a technique for generating and recording an X-ray pattern to provide the user with a static image(s) after the termination of the exposure. It is differentiated from fluoroscopy, mammography, and computed tomography. Radiography may also be used during the planning of radiation therapy treatment.
It is used to diagnose or treat patients by recording images of the internal structure of the body to assess the presence or absence of disease, foreign objects, and structural damage or anomaly.
During a radiographic procedure, an X-ray beam is passed through the body. A portion of the x-rays are absorbed or scattered by the internal structure and the remaining X-ray pattern is transmitted to a detector so that an image may be recorded for later evaluation. The recording of the pattern may occur on film or through electronic means.
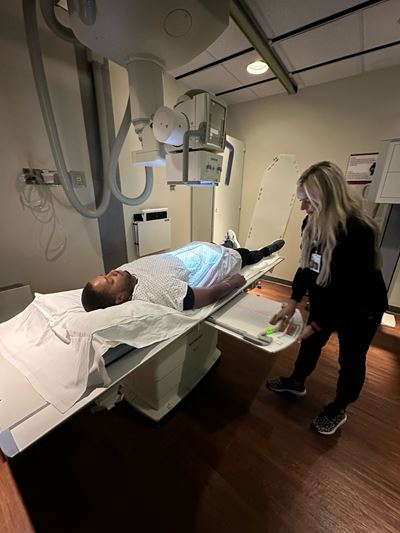
What is a Radiographer?
Radiographers are medical professionals tasked with operating highly specialized, state-of-the-art scanning machines. These healthcare professionals operate medical imaging equipment, while radiologists are primarily concerned with providing imaging interpretation. Once qualified, radiographers use scanning equipment that includes x-ray machines, computed tomography (CT scanners), and even advanced technologies such as digital fluoroscopy to produce specialized imaging.
Radiographers are primarily responsible for:
-
Properly preparing patients.
-
Verifying safety protocols are followed.
-
Knowing to operate a wide range of imaging devices.
-
Producing quality x-rays and images to ensure the right diagnosis can be made.
-
Following the supervision of a radiologist.
